Bank transactions are the lifeblood of personal and business finances. Without the ability to deposit, withdraw, and transfer funds, the modern economy would not function.
This guide will provide an in-depth look at everything you need to know about bank transactions – from what they are to how they work.
What is a Bank Transaction?
A bank transaction is any interaction that takes place between a customer and a bank or financial institution. Any time money is moved, whether it’s a deposit, withdrawal, funds transfer, or other activity – that is considered a bank transaction.
Bank transactions provide a record of money moving in and out of accounts. Analyzing transactions is key for both individuals and businesses to track finances, budgets, and cash flows.
Use AI to make your accounting tasks easier – Download this eBook today!
History and Evolution of Bank Transactions
Banking transactions have evolved significantly over time, shifting from simple deposits and withdrawals to complex digital transfers. Understanding this evolution provides insight into how bank transactions work today.
In ancient history, some of the earliest forms of banking involved temples and religious institutions providing loans of seeds, crops, and livestock. Repayment of these loans constituted simple transactions.

With the introduction of coinage in Lydia around 600 BC, banks began handling transactions in metal coins rather than commodities. Depositing and withdrawing coins became common transactions.

(Source)
During the Renaissance era from the 14th to 17th centuries, Italian banking families like the Medicis pioneered modern accounting practices. Handwritten records of all transactions in ledger books enabled better tracking of credits and debits.
(Source)
The 17th century marked the beginning of modern banking practices that would underpin today’s system. Banks in Amsterdam and London combined traditional banking functions like accepting deposits and lending with new innovative practices.
And as modern banking emerged in the 17th-19th centuries, transactions became more complex. Bills of exchange facilitated transfers between accounts internationally. Checks allowed cashless payments.

(Source)
The digital age brought major shifts. Electronic funds transfers enabled instant bank account transactions. Credit cards revolutionized consumer transactions in the 1950s.
Today, in the 2020s, transactions are conducted seamlessly online, via mobile apps, and at ATMs.
Emerging technologies like blockchain, cryptocurrency, and AI continue to transform modern transactions. Security enhancements like multi-factor authentication and end-to-end encryption safeguard today’s digital transactions.
Types of Bank Transactions
There are several common types of transactions that occur between banks and their customers. The main categories include:
- Deposits – Customers can make deposits into their bank accounts through methods like cash, check, or electronic transfers. Deposits increase the account balance.
- Withdrawals – Customers can withdraw funds from their accounts as cash, like at an ATM, or through transfers, checks, debit payments, or other methods. Withdrawals decrease the account balance.
- Transfers – Funds can be transferred between different accounts at the same bank or different banks, domestically or internationally. Transfers simply move funds between accounts.
- Loans and Credits – Transactional aspects of borrowing funds from a bank, including loan applications, disbursements to accounts, and repayments.
- Bill Payments – Transactions like checks, money orders, electronic payments, and transfers used to pay bills. Critical for managing finances.
- Foreign Exchange Transactions – Converting and transferring funds between different global currencies through banks.
- Fees and Service Charges – Banks deduct fees for services through transactions that reduce account balances.
- Interest Payments – Banks provide interest on deposits and charge interest on loans through transactions.
In summary, with the variety of transactions occurring in banking, such as deposits, withdrawals, transfers, and more, many of these are labeled with specific abbreviations in bank statements.
It’s a good idea to familiarize yourself with these abbreviations to better understand and manage these different types of transactions effectively.

Bank Transaction Regulations
Bank transactions are closely regulated to protect consumers and prevent financial crimes and 51% of firms said their biggest challenge is keeping up with regulatory change. (Accounting & Bookkeeping statistics)
Key regulations include:
- Consumer Protection Laws – Regulations like Truth in Lending Act and Electronic Fund Transfer Act establish rights and disclosures for consumers on transactions. Protect against unfair practices.
- Reporting Requirements – Banks must report certain large transactions to regulators and issue tax statements to consumers. Ensures oversight and compliance. (Source)
- Audits – Bank transactions are subject to internal and external audits to verify accuracy and compliance with regulations. Finds procedural issues. (Source)
- Anti-Money Laundering – Extensive regulations require banks to monitor transactions for suspicious activity that could indicate money laundering or terror financing. (Source)
- Fraud Prevention – Banks employ advanced analytics on transactions to detect potentially fraudulent activity and prevent losses. (Source)
- Privacy and Data Security – The Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act requires financial institutions – companies that offer consumers financial products or services like loans, financial or investment advice, or insurance – to explain their information-sharing practices to their customers and to safeguard sensitive data.
- Operational Controls – Stringent controls govern all stages of transaction processing for correctness, authorization, and compliance.
Following these regulations is essential for banks to maintain consumer trust, avoid penalties, and reduce financial crimes facilitated through bank transactions.
How to Get Bank Transactions?
Having access to bank transactions is getting easier day by day as banks and other financial institutions.
There are several ways individuals and businesses can access records of their bank transactions:
- Bank Statements – Banks issue monthly statements listing all bank transactions in an account over the past month. Statements may be printed and mailed or accessed digitally.
- Online Banking – Logging into online accounts provides real-time access to see recent transactions and download transaction history.
- Mobile Banking Apps – Banking apps also allow quick access to recent transactions and downloading transaction reports.
- Branch Visits – Visiting a local bank branch in-person also allows requesting transaction records and speaking with bank representatives.
- Downloading Reports – Banks allow downloading transaction data, often in formats like CSV, for import into accounting/finance software.
- APIs and Data Feeds – Businesses can use bank APIs to automatically retrieve structured transaction data for analysis.
Saving receipts, statements, and other transaction records is vital for budgeting, taxes, managing cash flow, and detecting any discrepancies.
Ensure that you have access to your bank transactions for at least 5 years in case of any needs.
In case your account is already closed, here you can learn how to get bank statements from a closed account.
How Are Bank Transactions Processed?
When a bank transaction is initiated, whether in-person, online, or at an ATM, it goes through a standardized process behind the scenes to complete it as well as protect all parties.
Here is the process:
- Authorization – The payer’s bank must authorize the transaction by verifying account funds, fraud checks, transaction limits, holds, etc.
- Clearing – The transaction details are submitted to a clearinghouse to confirm the payer, payee, account numbers, and amount.
- Settlement – The payer’s bank debits the account, the payee’s bank credits the account, and funds are transferred through the clearinghouse.
- Posting – The completed transaction is posted to the customer’s account ledger and reflected in the account balance.
- Documentation – Receipts, transfer confirmations, statements, and other documentation is generated for record keeping.
- Archiving – Transaction details are stored long-term by the bank for compliance and retrieval if needed.
Automated systems handle much of this process in real-time or batch processing.
Additionally, strict controls are followed to verify identities, prevent duplication, and protect funds at each step.
Also, audits help verify all procedures are followed.
Understanding this backend process helps explain why transactions may take time to complete, for example waiting for checks to clear. It also builds trust in the safety of bank transactions.

How to Get Bank Transactions from PDF Statements?
PDF bank statements contain important transaction details, but aren’t easy to work with compared to Excel or CSV files.
Luckily, optical character recognition (OCR) technology can automate converting PDF bank statements into more usable formats.
Here’s an overview of the process:
- Use a bank statement converter tool that supports OCR – This will recognize text in scanned or image-based PDF statements. Popular options include DocuClipper.
- Upload the PDF statements – Drag and drop or browse to select PDFs from your computer to upload. Many tools support batch uploading multiple statements.
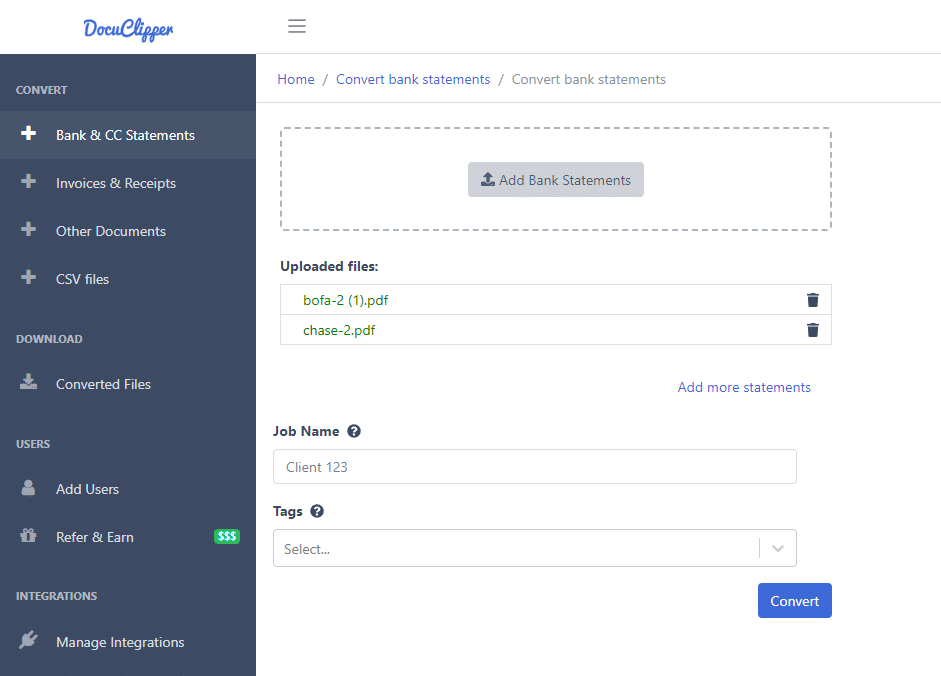
- OCR extracts the transactions – Behind the scenes, OCR will identify and extract key data like dates, amounts, descriptions into structured data to create bank extract.
- Review and reconcile transactions – The tool may provide options to review, reconcile with statement balances, and check for duplication. This verifies OCR accuracy.
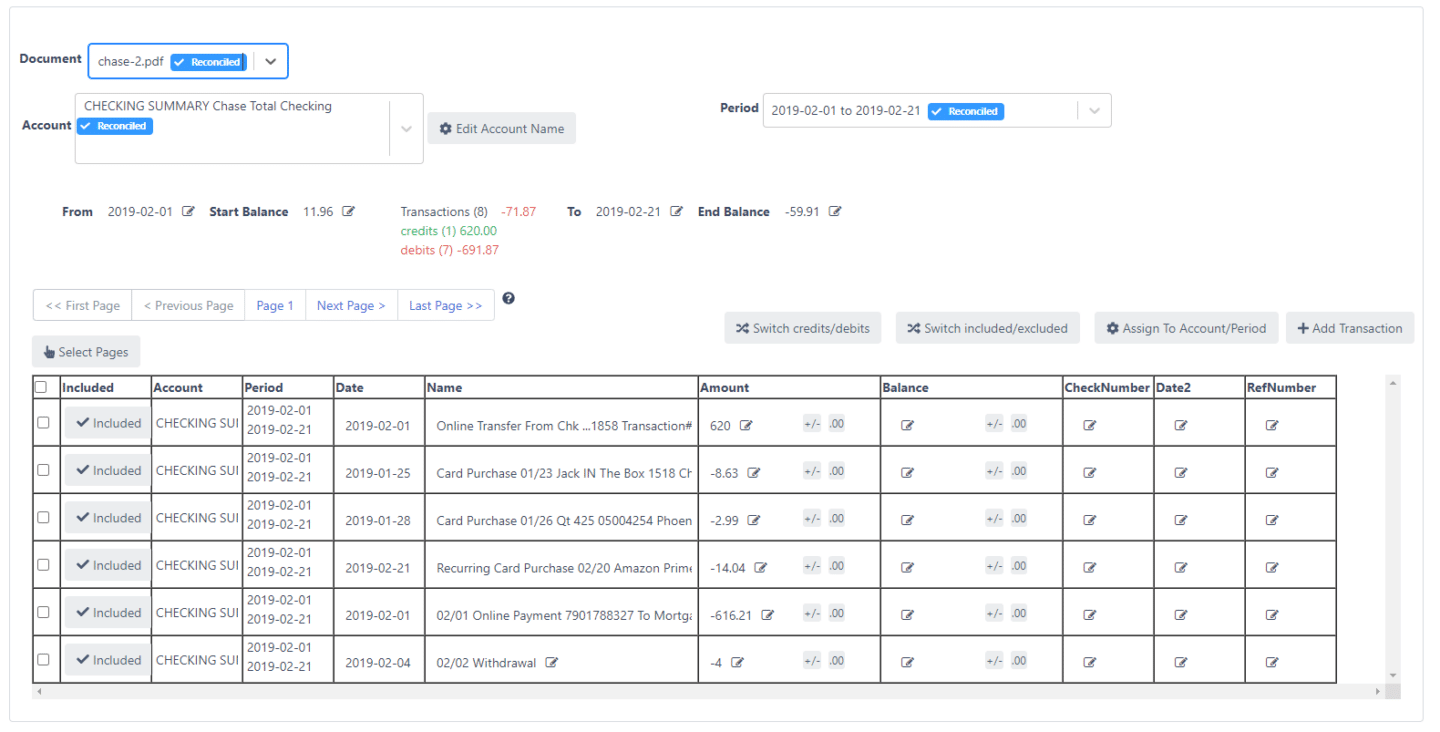
- Download the converted data – Extracted transactions can be downloaded in formats like Excel, CSV, or imported into accounting software like Quickbooks.
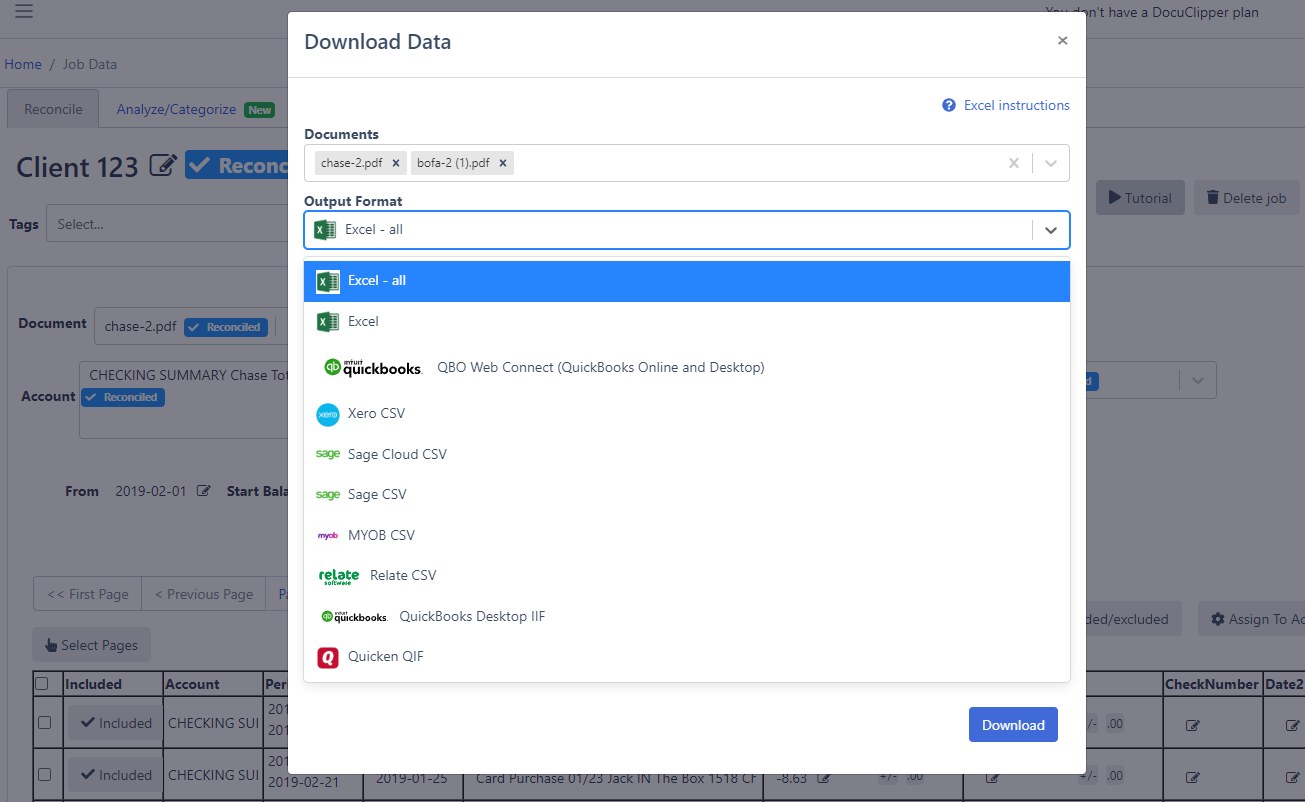
- Customize the output – Choose which fields to include and how to structure the converted data for your workflow.
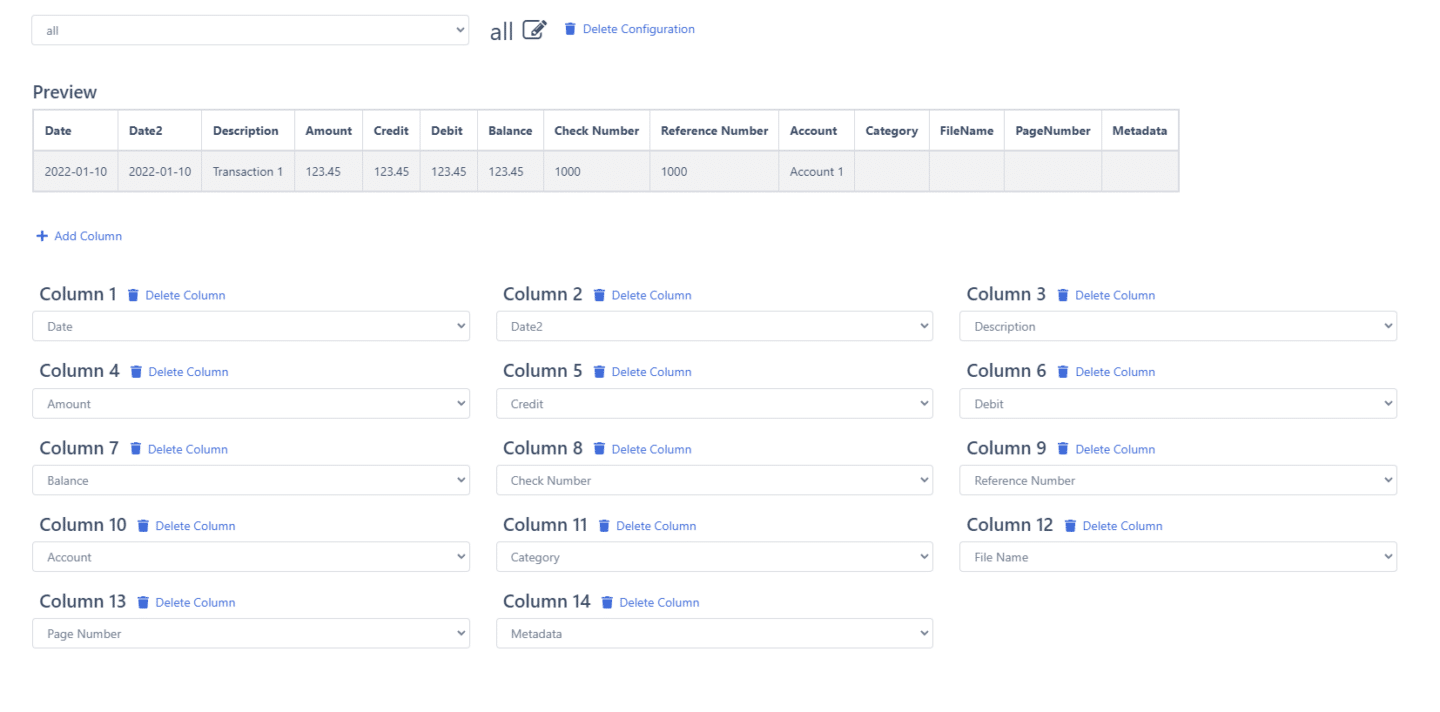
Converting PDF bank statements into editable Excel or CSV files makes it much easier to work with the data for budgeting, accounting, taxes, underwriting, and managing your finances. The right OCR tool saves tons of time.
To learn more about:
- How to convert PDF bank statements to Excel or CSV
- How to convert CSV statements to QBO
- How to convert PDF statements to QBO
How to Reconcile Bank Transactions from PDF Statements?
Reconciling transactions from PDF bank statements involves comparing the statement data to your own financial records to verify accuracy.
Here are the key steps:
- Convert the PDF Statement to Excel/CSV
Use a PDF converter tool or bank statement parser to extract the transaction data from the PDF statement into a formatted Excel or CSV file. This structures the data for easier reconciliation.
- Match Transactions to Accounting Records
Compare the statement transactions to transactions recorded in your accounting software, spreadsheet, or other ledger. Match up deposits, withdrawals, fees, etc.
- Identify any Discrepancies
If any statement transactions are missing from your records or don’t match, identify these discrepancies for further inspection.
- Research Discrepancies
For any discrepant transactions, research the details from both statement and records to determine the cause. This may involve contacting your bank.
- Make Adjusting Entries
If errors are identified, make adjusting entries in your accounting records to correct the discrepancies and match the statement.
- Confirm Balances Match
Finally, verify that the ending statement balance and your adjusted account ledger balance match, confirming reconciliation.
Frequently Asked Questions about Bank Transactions
In this section we’re going to answer relevant questions to bank transactions
What are the bank transactions?
Bank transactions are exchanges of money between a customer and a financial institution or between internal bank accounts. Common types of bank transactions include deposits, withdrawals, transfers, loan disbursements, loan payments, account fees, and interest payments or earnings. These transactions allow customers to manage funds, access credit, and facilitate financial activities through their bank accounts. Efficient processing of transactions is central to a bank’s operations.
What are the three main types of bank transactions?
The three main types of bank transactions are deposits, withdrawals, and transfers. Deposits put money into an account, withdrawals take money out, and transfers move money between accounts.
How many transactions are there in a bank account?
There can be unlimited transactions in a bank account over time. Common transactions include deposits, withdrawals, transfers, fees, interest, checks, and debit card purchases. The number of transactions reflects the account’s usage.
Can my bank see all my transactions?
Yes, a bank can see all transactions occurring in your accounts. This allows them to provide account balances, statements, fraud monitoring, and other services. The transaction history is accessible to bank staff through the core banking system.
How do I provide bank transaction history?
To provide bank transaction history, request monthly statements from your bank. Many banks also have online banking portals allowing you to export detailed transaction reports. You can share these with third parties requiring verification.
How can I get a bank transaction history?
You can get your bank transaction history by logging into online banking and accessing your account statements and transaction reports. Or visit your bank branch and request copies of past statements. The statements will provide all deposit, withdrawal, and transfer activity.
Conclusion
Bank transactions are essential for managing personal and business finances.
Properly recording and managing transactions enables tracking of cash flows, budgets, taxes, and financial positions.
Additional resources for learning more include FDIC.gov for US banking, AccountingTools.com for reconciliation processes, and ConsumerFinance.gov for transaction regulations.
By understanding all aspects of bank transactions, individuals and businesses can optimize their financial operations.
Related Articles
- How to Import Bank Statements into QuickBooks Online
- How to Convert Credit Card Statements to Excel or CSV
- 10 Best Bank Statement Converter Software
- How to Categorize Transactions
- How Long to Keep Bank Statements?
- How to Perform Bank Statement Verification
- How to Perform Bank Statement Income Verification