Choosing OCR vs IDP has been a tough choice for many people. With much technology available today, companies, businesses, and professionals have a lot of options to choose from in maximizing their efficiency.
This blog will talk about the pros and cons of OCR and IDP and its practical uses within the industry. It also talks about the potential future of these technologies and their contributions to businesses and professionals.
Key Takeaways:
- OCR is affordable and fast, ideal for converting images and PDFs to text, with high accuracy for formatted documents but struggles with complex fonts and languages.
- IDP offers enhanced accuracy and automation, using AI for advanced document processing, capable of learning and adapting over time, but it’s more expensive and requires more data.
- OCR is suitable for simple document digitization, making it easy to manage and retrieve data, while IDP excels in analyzing and extracting insights from complex documents.
- IDP builds on OCR’s capabilities, analyzing and extracting valuable information after OCR digitizes the text, integrating both for a comprehensive document management solution.
- Choosing between OCR and IDP depends on specific needs: OCR for straightforward digitization and IDP for in-depth analysis and automation in handling complex documents.
What is OCR?
OCR (Optical Character Recognition) is a technology that converts different types of documents into editable and searchable data. It recognizes text within a digital image and translates it into a machine-readable form.
It is used in many fields like finance, accounting, and statistics. The leading tools in accounting are OCR bank statement converters that use OCR to process bank statements and invoices.
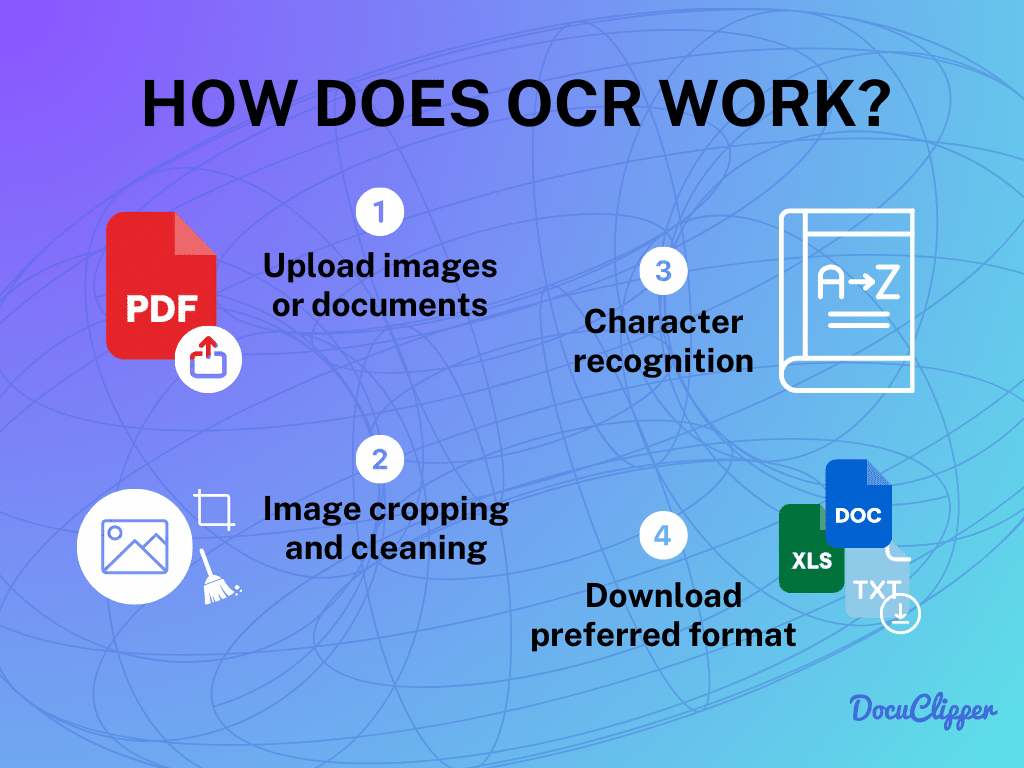
Benefits of OCR
OCR is great for turning images and PDFs into text. It’s easy to use, accurate, and not too pricey, which is why lots of companies like it.
Let’s look at its good points.
- Very Affordable: OCR data capture solutions range from free to moderately priced, making them accessible for individuals and businesses of all sizes.
- High Accuracy for formatted OCR: When trained with specific fonts and formats, OCR can achieve very high accuracy levels.
- Easy to Implement: OCR technology is straightforward to implement, often requiring minimal setup and training.
- Very Mature Technology: OCR has been around for decades, leading to a well-developed technology with extensive support.
- Very Fast in Processing: OCR can process documents rapidly, often taking just seconds to extract data from documents.
Limitations of OCR
OCR sometimes struggles with fancy fonts, some languages like Japanese or Chinese, or smudged prints and can’t always understand context like IDP.
Here, we’ll see where it falls short.
- No Self-Learning: Traditional OCR does not improve over time or adapt to new formats automatically, it has to be adjusted by the developers.
- Specialized OCR required for specific documents: For complex or unusual documents such as bank statements, specialized OCR solutions may be required.
- No Insights: OCR only converts text; it does not provide insights or analysis of the data converted.
- Limited to Language & Fonts: OCR accuracy can decrease with less common languages and unusual fonts.
What is IDP?
IDP (Intelligent Document Processing) uses a combination of OCR, artificial intelligence, and machine learning to automate the processing and extraction of information from a variety of document types.
IDP is commonly used in analyzing data. It processes data quickly and provides instant, insightful analysis.
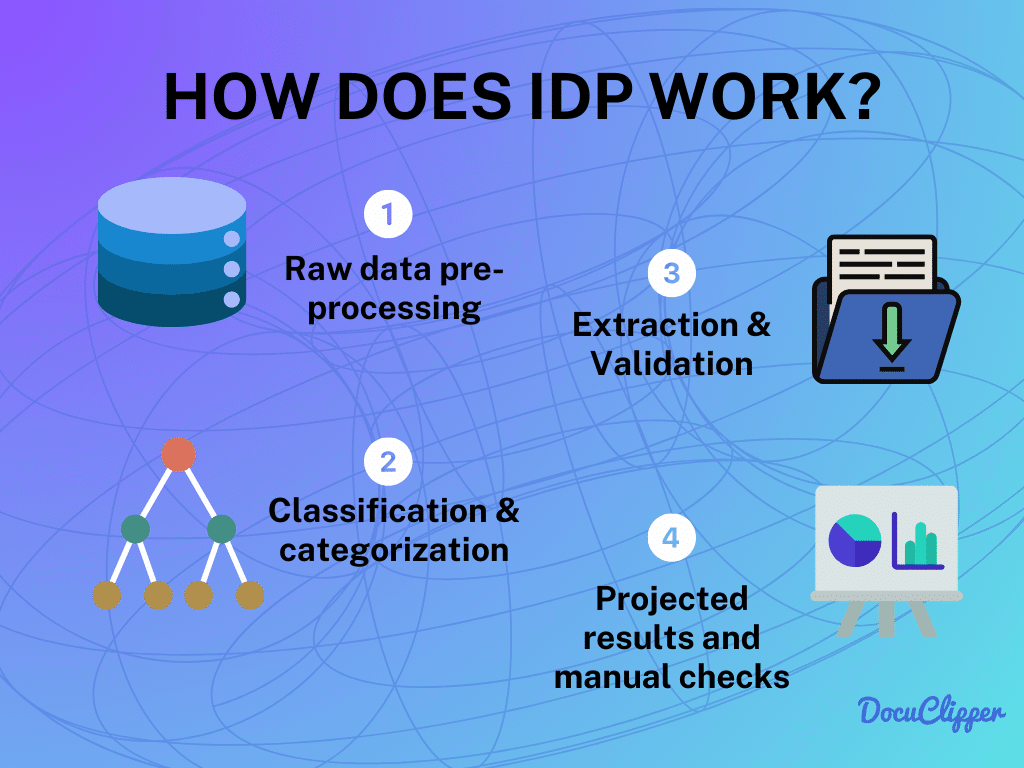
Benefits of IDP
IDP uses AI to revolutionize document handling, offering superior understanding, reduced errors, and improved efficiency. This brief overview highlights why IDP is a game-changer in document management.
- Enhanced Accuracy Across Different Documents: IDP offers improved accuracy, especially with complex or varied document formats.
- Improved Processing Accuracy: The integration of AI and ML leads to a more accurate data extraction process than OCR data extraction.
- Improved Data Insights: IDP can provide valuable insights from the processed data through statistical analysis
- Self-Learning: IDP systems can learn and adapt over time, improving their performance in the long run.
- Fully Automated: Offers a higher level of automation in document processing compared to traditional OCR software.
Limitations of IDP
Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) uses AI to handle documents better than older OCR systems, but it’s not perfect.
It can be pricey, might learn biases, can be tough to add to current systems, needs a lot of data, and is usually slower than OCR. Let’s look into these issues.
- Higher Cost: IDP solutions are typically more expensive than basic OCR systems.
- High Potential for Bias: AI algorithms can inadvertently learn biases present in the training data.
- Difficult with Integrating with Existing Systems: Integration with existing systems and workflows can be challenging.
- Needs Large Training Data: Effective IDP requires substantial training data to achieve high accuracy.
- Slower Than OCR: Generally, IDP processes documents more slowly than OCR due to the complexity of the tasks involved.
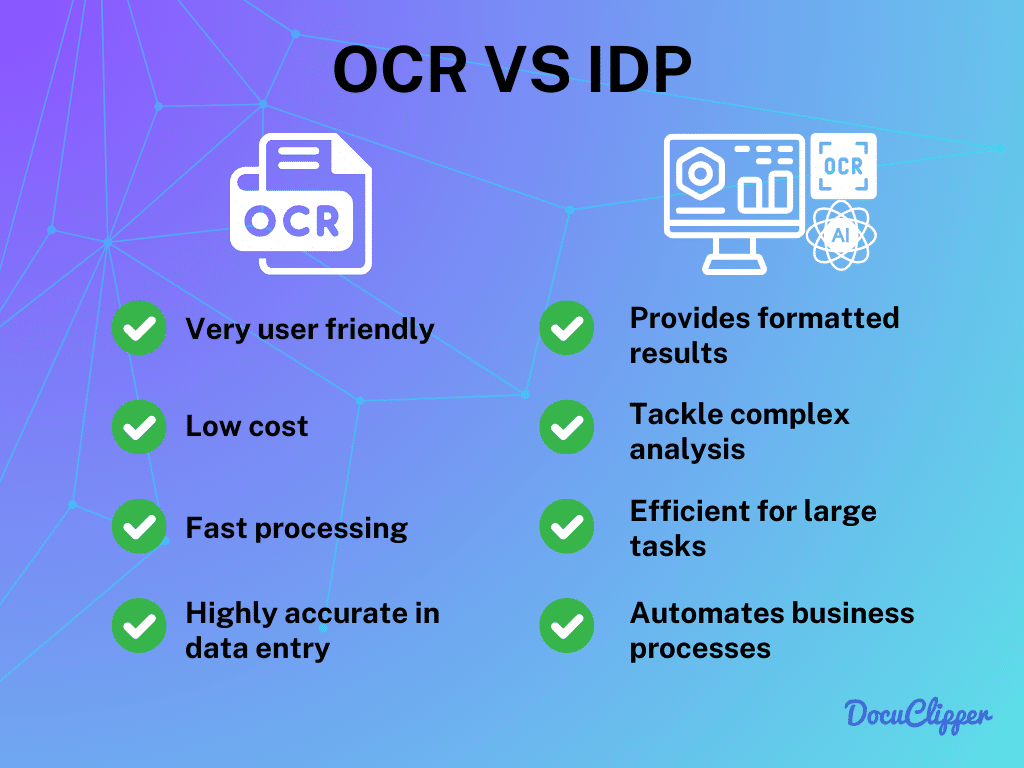
Main Differences Between OCR & IDP
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) are crucial tools in today’s world of document management, but they each have their roles and use different technologies.
OCR is all about turning documents into digital text, making it easy to convert printed pages into a format that computers can understand. IDP goes a bit beyond that. It doesn’t just convert the text; it also uses advanced AI to analyze the data and transform it into insights.
Knowing how these two differ is important when deciding which one to use for your specific needs in handling documents.
| OCR | IDP | |
| What it does | Converts various document types into editable and searchable data. | Automates the processing, extraction, and analysis of information from documents using AI. NLP, ML, and OCR. |
| How it works | Uses software to identify text characters and format document images, converting them into digital text. | Combines OCR, AI, machine learning, and NLP to capture, extract, and process data from various document types. |
| Technology | Optical Character Recognition (OCR) uses image processing and pattern recognition to turn pictures of text into digital text. | AI technologies like Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Computer Vision, alongside Deep Learning and Machine Learning (ML). |
| Accuracy | High for clear, well-formatted text; varies with input quality and complexity. | Highly accurate for structured and semi-structured documents; continually improving for unstructured documents. |
| User Experience | Generally user-friendly with simple operation, depending on the software interface. | Streamlined and automated, though initial setup and training can be complex. |
| Cost | Range from free for basic applications to significant investment for advanced solutions. ranging From $20 to $100 | Generally higher than OCR due to advanced technologies; efficiency can offset costs. |
| Processing Speed | Fast, processing pages within seconds; varies with document complexity. | Fast and efficient for repetitive and large-scale tasks; influenced by document complexity and AI sophistication. |
| Scalability | Easily scalable, especially cloud-based solutions for handling increased volumes. | Highly scalable, particularly suitable for large volumes of documents and cloud-based solutions. |
| Typical use cases | Data entry automation, Converting bank statements and financial information, digitizing documents, processing IDs, converting books, etc. | Used in banking, insurance, legal, and healthcare for processing forms, invoices, contracts, records, etc. |
| Future-Readiness | Evolving with AI advancements; expected to become more accurate and versatile. | Poised for growth with AI advancements; expected to handle more document types and complexities. |
OCR is an easy and affordable way to turn text from paper documents into digital text. It works well with clear and simple documents, is quick, easy to use, and can handle lots of data, making it great for jobs like typing up information and turning old documents into digital ones.
On the other side, IDP uses smart tech like AI to be more precise and thorough, especially with complicated or different kinds of documents. It costs more and is a bit harder to set up, but it gives you a deeper understanding and can do things automatically.
Examples of OCR and IDP
OCR and IDP are well been used throughout the industry ranging from finance to data science. Here are some cases:
Processing Bank Statements
- OCR: This tool is great for scanning and converting paper bank statements into digital text. It’s precise in recognizing numbers and text, making it easy to store these statements digitally for quick access and searchability in bank statement audits.
- IDP: IDP takes it a step further. It undergoes bank statement analysis to extract crucial financial information such as account balances, transaction details, and spending patterns. Moreover, it can automatically categorize bank transactions and integrate this data with financial management systems for deeper analysis.
Processing Financial Data
- OCR: It plays a crucial role in converting paper-based financial records into digital formats. This includes documents like financial reports, balance sheets, and more, making them easier to manage and retrieve.
- IDP: IDP not only digitizes these records but also analyzes them. It can identify trends, spot discrepancies, and ensure compliance, providing a comprehensive view of financial data.
Processing Invoices
- OCR: For invoices, OCR quickly extracts data from invoices into searchable digital text. This is especially useful for processing invoices.
- IDP: After the invoices are digitized, IDP can extract important details like vendor information, invoice amounts, due dates, and itemized charges. This facilitates automated invoice processing and integration with accounting systems.
Analyzing Financial Statements
- OCR: OCR is used to digitize printed financial statements, making them accessible in a uniform digital format.
- IDP: Going beyond mere digitization, IDP tools analyze these statements, extracting key metrics such as revenue growth and profitability. This enables more informed financial decision-making and thorough trend analysis.
How do OCR and IDP Work Together?
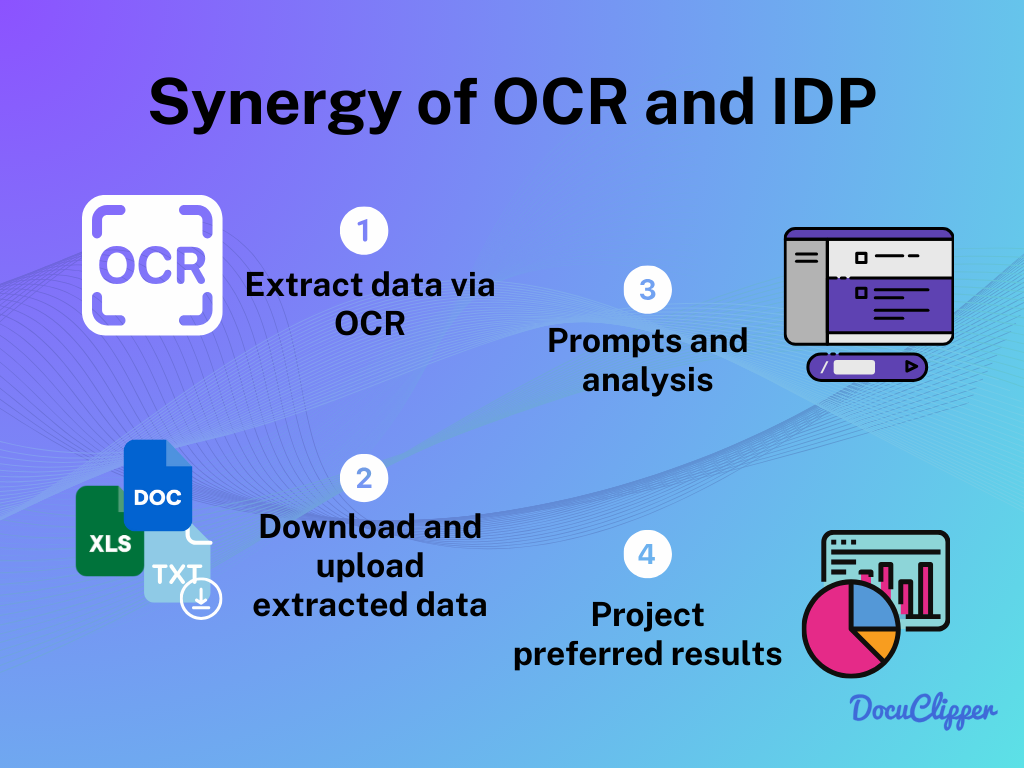
How does OCR work with IDP to make handling documents easier and more efficient? First, OCR takes any paper or picture of a document and turns it into text that a computer can read. This is a really important step for any document that’s not already in a digital form.
After OCR has changed the document into digital text, IDP steps in. IDP uses smart technology like AI to do more than just read the text. It understands, interprets, and analyzes the information in the document. This means it can find and use the important parts of the text.
The way OCR and IDP work together is like a team. OCR starts the process by making the documents digital. Then, IDP takes over and uses this digital text to do more advanced things like sorting information and finding patterns.
Conclusion
In data management, OCR and IDP each have their special roles. OCR is simple and budget-friendly, good for turning written documents into digital text. It’s great for straightforward tasks as well as for automated bookkeeping processes.
However, OCR has its limits – it doesn’t learn or give insights on its own. That’s where IDP comes in. IDP takes what OCR does and adds smarter features like AI. This means it can understand and analyze documents better, especially complicated ones.
So, while OCR is good for basic digitizing, IDP goes a step further, making it a better choice for more complex needs and future technologies.
Convert & Process Bank Statements with DocuClipper
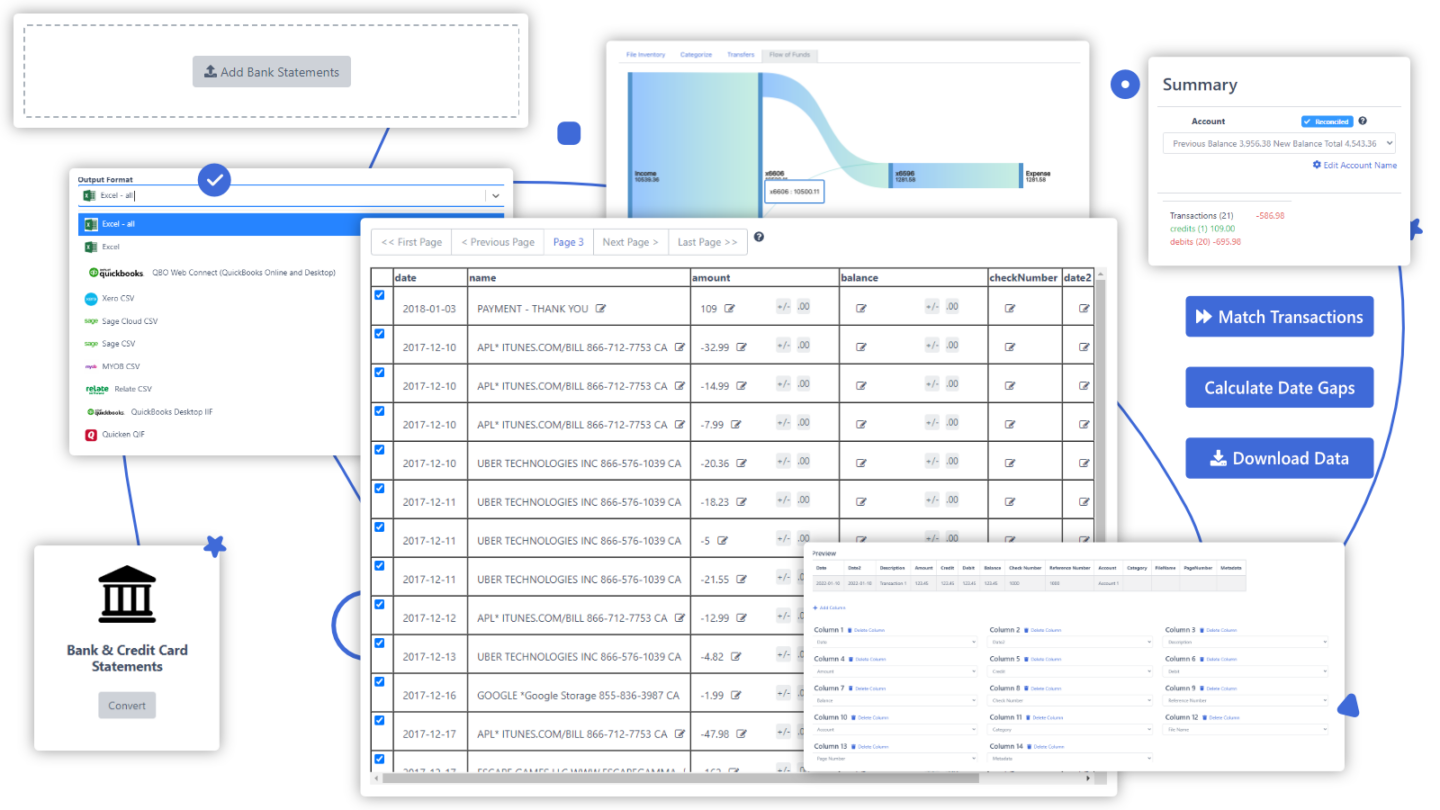
Check out DocuClipper for quick and precise bank statement conversions. It’s perfect for analyzing bank statements, with tools for reconciling accounts and sorting transactions.
In just 20 seconds, DocuClipper delivers results with 99.99% accuracy, and you can export data in formats like CSV, XLS, and QBO.
FAQs about OCR vs IDP
In this section we’re going to answer commonly asked questions about OCR vs IDP and related:
What is the difference between OCR and IDR?
OCR converts images of text into machine-readable text, focusing on the digitization of documents. IDR, incorporating OCR, adds an understanding of context and structure, using AI and other software to interpret and extract meaningful information.
What is the difference between OCR and document AI?
OCR is a technology for converting text images into editable formats, primarily focusing on text digitization. Document AI, which includes OCR, applies AI to understand, interpret, and extract insights from document data.
Why is OCR better than IDP?
OCR is simpler and more cost-effective for basic text extraction from documents. It’s suitable for straightforward digitization needs without the requirement for advanced data interpretation.
Why is IDP better than OCR?
IDP offers advanced processing by understanding context and automating document-based tasks, going beyond mere text conversion. It’s ideal for complex tasks needing data validation and decision-making based on document content.
Is OCR an AI?
Traditional OCR is not AI; it’s a process for converting text images into editable text. However, modern OCR may incorporate AI elements for improved accuracy and context understanding.
Related Articles:
- Purchase Order vs Invoice: What are the Differences
- OCR vs AI: 7 Differences, Pros, Cons, & Which to Choose
- How to Categorize Transactions for Bank and Credit Card Statements [6 Ways]
- Bank Statement Audit: Essential Guide for Accurate Financial Analysis
- How To Automatically Categorize Bank Transactions in Excel: Template Included